Are plastic energy chains resistant to hot chips?
The material of which igus e-chains are made has to cope with a great deal of stress such as pressure and tensile strain, and must be abrasion-resistant, very sturdy and have a high modulus of elasticity, whereby it must also exhibit stable behaviour at high and low temperatures and be resistant to hot chips.
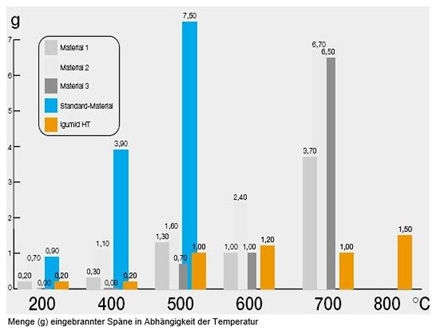
As a rule, the standard temperature range for plastic energy chains is -40°C to +130°C, short term +170°C. A red-hot chip, however, is considerably hotter, usually above 800°C.
igus uses a special method to treat HT products so that the treated products can withstand short-term temperatures above 850°C. A red-hot chip can therefore no longer fuse with the plastic, as a result of which the e-chain can be used directly in areas where chips occur. In 90% of all cases, it is sufficient if only the lid and floors are made of HT material as they present the largest attack surfaces. Most e-chains and e-tubes can be made of HT material.