Plain bearing materials in comparison: metal-polymer plain bearings
Lars Butenschön | 6. May 2021
In this section of our series of articles on the subject of plain bearing materials, we look at the so-called metal-polymer plain bearings. What are metal-polymer plain bearings? How do they differentiate themselves from other types of bearings? What are they particularly good for and when is it better to leave them alone?
In this blog post, we take a literal look at metal-polymer plain bearings and weigh up the specific advantages and disadvantages compared to other plain bearing materials.
Why are there metal-polymer plain bearings?
Metals, more precisely steels, bronze, copper or brass are common materials in the plain bearing sector due to their load-bearing capacity and thermal conductivity. To improve their sliding properties and wear resistance, plain bearings made of these materials are usually lubricated. The problem: grease or oil lubrication requires sophisticated feed systems in the bearing points (lubrication grooves and grease nipples, central lubrication) in terms of production technology. In addition, the lubricants often get into the environment and contaminate surrounding components or products. In the search for alternative technologies to reduce the coefficient of friction, a special plastic was finally found at the beginning of the 20th century that had excellent sliding properties: polytetrafluourethylene, or PTFE for short, and better known under the trade name of the DuPont company, Teflon.
The problem: Teflon not only offers excellent sliding properties, but is also extremely soft. So if it were possible to combine the stability of metal with the sliding properties of a plastic such as PTFE, lubrication could be dispensed with. The concept: a hard-wearing metal shell protects an embedded layer of PTFE. But how do you get such a well-sliding and accordingly poorly adhering material to stick to the metal?
Refined technology in detail: metal-polymer plain bearings
The greatest strength of metal-polymer bearings is also their greatest weakness. The lubricating or better sliding film made of particularly slippery and correspondingly soft plastics. These include PTFE, but occasionally also other plastics such as polyoxymethlyene (POM). With the skilful combination of different manufacturing methods and materials, the fixation of these plastics in the protective metal sleeves is successful. The enlarged view of these bearings provides information.
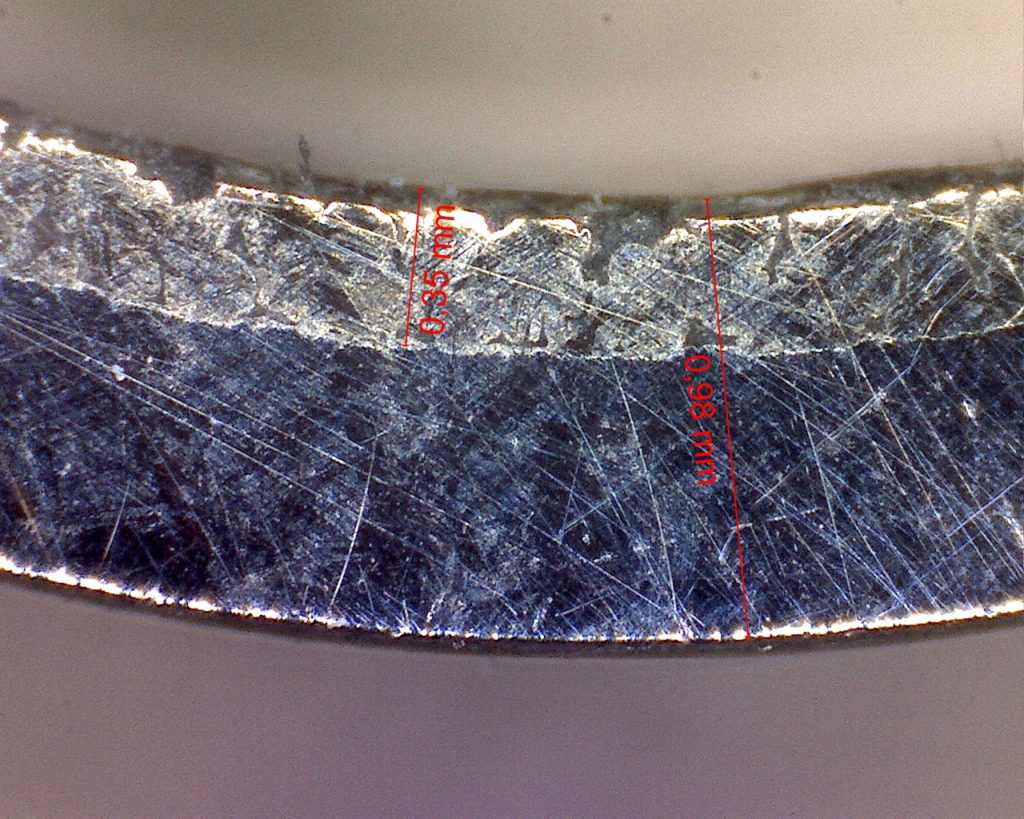
The PTFE layer, which is extremely thin compared to the wall thickness of the metal sleeve, is not applied directly on the steel. Instead, it is applied to a porous layer of sintered bronze, which in turn adheres to the steel.
The advantages and disadvantages of metal-polymer plain bearings
The advantages and disadvantages of this type of plain bearing result from this multi-layer structure. The main advantage: metal-polymer plain bearings – at least those with a PTFE gliding layer – operate “dry”, i.e. without grease or oil lubrication. The PTFE layer ensures a relatively low coefficient of friction. Due to the high metal content, heat dissipation is also better compared to all-plastic plain bearings. Last but not least, the load-bearing capacity is very high due to the steel used. Static loads in particular can be absorbed well in this way.
The main disadvantages of metal-polymer bearings are the susceptibility of the used steel to corrosion and the lead contained in some variants, which disqualifies them from the RoHS certification. In addition, the weight is high compared to all-plastic plain bearings.
The main limitation, however, is precisely the PTFE layer necessary for the good sliding properties. If this extremely thin layer is damaged or scratched due to improper installation or run down due to increased wear, the shaft to be supported runs on metal. Worn bearings do not just result in a little more bearing clearance, but often cause direct damage to the shaft, which is often relatively expensive. In addition, due to the manufacturing process, the design of the plain bearings is limited to shapes that can be cut or bent from rolled sheet metal.
Advantages:
- High static loads possible
- Comparatively good heat dissipation
- Low coefficient of friction (PTFE)
Disadvantages:
- Thin, sensitive PTFE layer
- Susceptible to corrosion
- Some variants not RoHS compliant
- Comparatively high weight
- Restricted design
Looking for the optimum plain bearing? We would be glad to assist you!
In every plain bearing application, these advantages and disadvantages have to be weighed up against each other. By no means all of these aspects play a role in every application. In addition to metal-polymer plain bearings, there are other bearing types that have different strengths and weaknesses.
Different types of plain bearings are suitable for different applications in different specifications. Often there is an overlap of applications – but it is not uncommon for there to be major differences in service life and performance.
Our application specialists will be happy to advise you and design your bearing point together with you. We will determine the plain bushing with the best ratio of service life, costs and performance for you – by telephone, via digital visit or at your site. Free of charge and without obligation. Everything from one source.
