Why blockchain is the next step for IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things)…!
Richard Habering | 17. November 2022
When it comes to blockchain, most people think of cryptocurrencies or NFTs, and with good reason. The crypto universe is bigger than ever and has gained the attention of the masses in recent years. However, blockchain technology can also be used for other, less well-known applications, of which integration with the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the most promising. This blog will showcase the benefits of blockchain for the IIoT and present examples of applications that combine both.
What is the blockchain?
The blockchain itself is an immutable, shared ledger that can be used to track and record assets and transactions. These assets can be almost any physical or digital product. What makes blockchain unique is the fact that it is immutable. This is achieved through the way transactions are recorded. Each transaction is recorded as a “block” and contains all relevant information required. Each newly recorded block is cryptographically secured to the block before and after it, with accurate timestamps confirming when the transactions took place. As more blocks are added, the chain (hence the blockchain) becomes larger and more secure. Once recorded, a transaction cannot be reversed. The only way to achieve this is to record new transactions that reverse the outcome of the original transaction. However, every transaction would be permanently linked to the blockchain and could be traced at any time1.

So how can this be of use in the world of IIoT? Quite simply, the IIoT is based on the collection, storage, transmission and application of data through condition monitoring and predictive maintenance. With the blockchain, this data can still be processed as usual, but with the added security and efficiency that the blockchain offers. No single user can make changes to previously recorded blocks, so everyone viewing these transactions and information can be sure they are correct. In addition, transactions can be easily viewed by all members of the network, which improves transparency and eliminates redundancies.
Smart contracts
Before we delve into potential applications of blockchain-based IIoT systems, it is important to understand smart contracts and how they work in these applications. Smart contracts are one of the key functions of blockchain. Simply put, a smart contract is an automated “contract” that is executed when certain criteria are met2. For example, a smart dishwasher connected to the blockchain could use the smart contract to automatically place an order for detergent when it is about to run out. A vending machine could even be used as a basic model for a smart contract: if the specified criteria are met (money has been inserted and a button has been pressed), an automated action is performed3. Since the process is automated and based on predefined criteria, concerns about accuracy and timelines are eliminated.
Blockchain applications in IIoT systems
Finally, it is time to discuss specific ways in which blockchain can be implemented and integrated into the IIoT to create more efficient information networks. Food production is an important industry that blockchain-based IIoT technology could revolutionise. Imagine, for example, that a foodborne illness has contaminated food somewhere in the supply chain. Once it is determined that the food is contaminated (usually after consumers become ill), a great deal of time must be spent determining exactly what food was contaminated and when. Meanwhile, more people might unknowingly buy the contaminated food and get sick. With a blockchain-based system, it would be easier and faster than ever to find the origin of the contamination. To this end, components with intelligent sensors would employ condition monitoring throughout the supply chain. Using these detailed records, the blockchain could conduct surveys to find out where and when the contaminated food was bought or consumed, and how many people became ill. In this way, it would be possible to determine exactly when and how the contamination began, and to take action quickly4.
Smart grids are another application area that would benefit significantly from blockchain. Smart grids are a decentralised peer-to-peer alternative to traditional electricity grid systems that allow individuals to generate and sell electricity. Thus, large energy utility companies are not the sole source of electricity5. Most small-scale power generation uses renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind, which makes them more environmentally friendly than larger power generators.
A key factor in making smart grids feasible is the IIoT. Smart meters equipped with IIoT sensors can communicate via cellular and radio frequency technology to automatically reroute power in the event of an outage without humans having to do so in person. These sensors also provide constant data on electricity consumption and demand, making it easier for utilities to respond to or predict rapid changes in demand than would be the case in traditional power grids6.
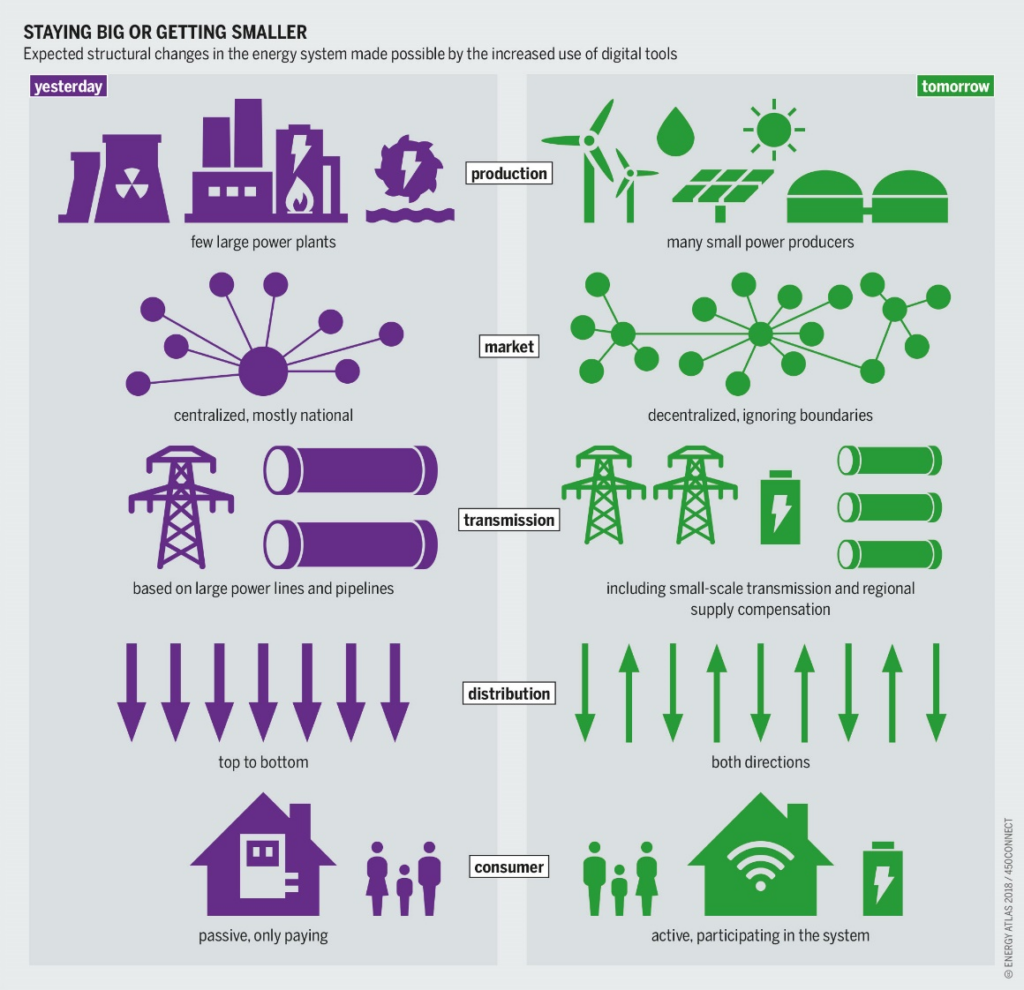
Smart grids use prepaid pricing models, so there must be a way to ensure that electricity is delivered after payment is received. This is where the smart contract steps in. In smart contracts, both the payment and the delivery of electricity are carried out automatically and are visible to users of the blockchain. Disputes can be easily resolved thanks to the way transactions are recorded. With most blockchain networks, an internal audit can even be integrated into the framework, making the system even more reliable7.
As blockchain and the IIoT grow, so do the potential applications for it. Integrating blockchain into the IIoT is the next logical step in advancing any industry, and for most users, it can turn blockchain into more than just a platform for cryptocurrencies.
Do you have questions about implementing IIoT in your application? Talk to an igus® expert today or visit our website.
- Sources:
- 1. https://www.ibm.com/de-de/topics/what-is-blockchain
- 2. https://www.ibm.com/de-de/topics/smart-contracts
- 3: www.techtarget.com/searchcio/feature/Examples-of-smart-contracts-on-blockchain
- 4: ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=8917991
- 5: www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319157819309000
- 6: www.digi.com/blog/post/what-is-the-smart-grid-and-how-enabled-by-iot
- 7: www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/risk/articles/internal-auditing-guide-to-blockchain.html

