How does a gear work?
Simply explained, a gear is a wheel, along the outer edge of which serrations are attached. Two gears whose teeth are identical in shape and gap, can run against each other and thus transmit power from one to the other gear. The gears with the same toothing can have different sizes.
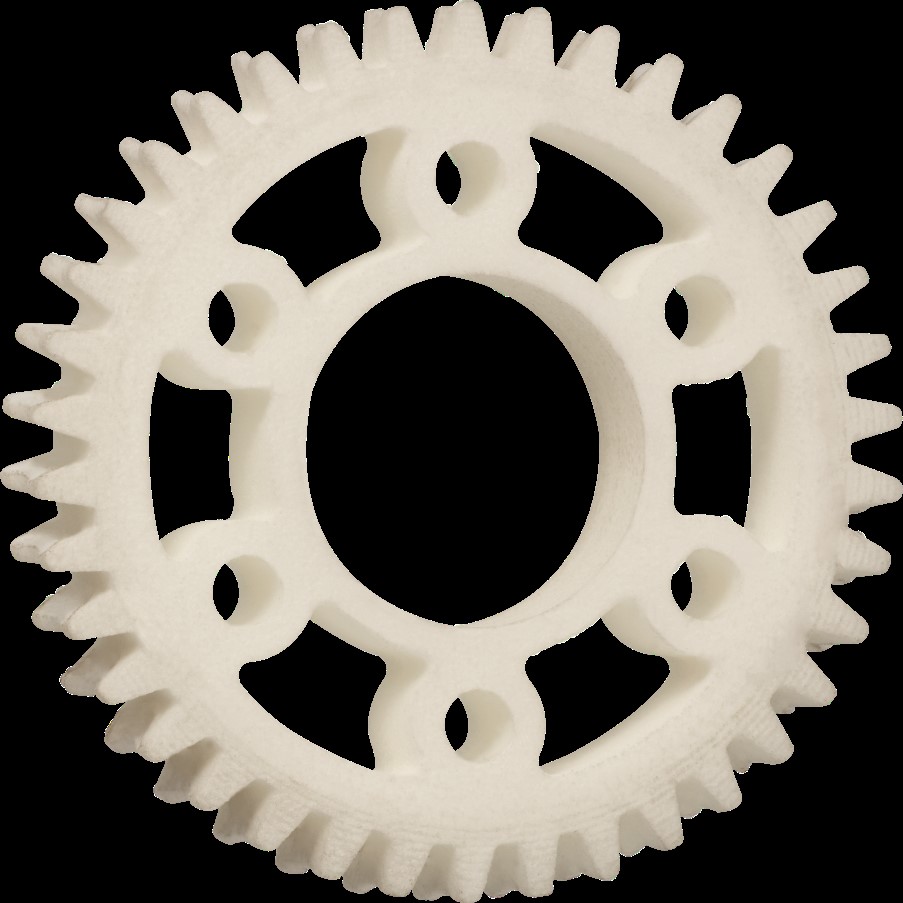

With two interlocking gears, the first presses the teeth of the second in one rotation, so that it also rotates. In this case, the second gear moves in the opposite direction of the first. This technique is used to transmit power from a drive shaft via a gear to a second gear and its shaft. This is called tooth gear.
Alternatively, the driving force can be transmitted to another gear in the form of torque and speed, for example also via a chain (e.g., bicycle). Torques and speeds can be changed in a gear pair. For this, only gears of different size and number of teeth have to be combined.
Gear drives are the most widely used and most commonly used transmission type.
Advantages of 3D printing in the manufacture of gears
The advantage of the 3D printing process for the production of gears is the ability to optimally model the shape of the tooth compared to injection moulding or milling. Thus, the shape of the teeth can be improved so that a more flat interlock and thus a better pressure distribution is generated. This is a great advantage and extends the service life of the gear compared to conventional manufacturing processes. If wear-resistant plastics are used, the durability is further optimised.

Would you like to calculate the service life of gears made by 3D printing? Our service life calculator will help you.
Click here for Service life calculatorfor gears
Do you need a gear, but do not have a CAD file yet? In our gear configurator, you can create the file and then order it at our 3D printing service.
Go to the configurator for gears
And here to our 3D printing service
