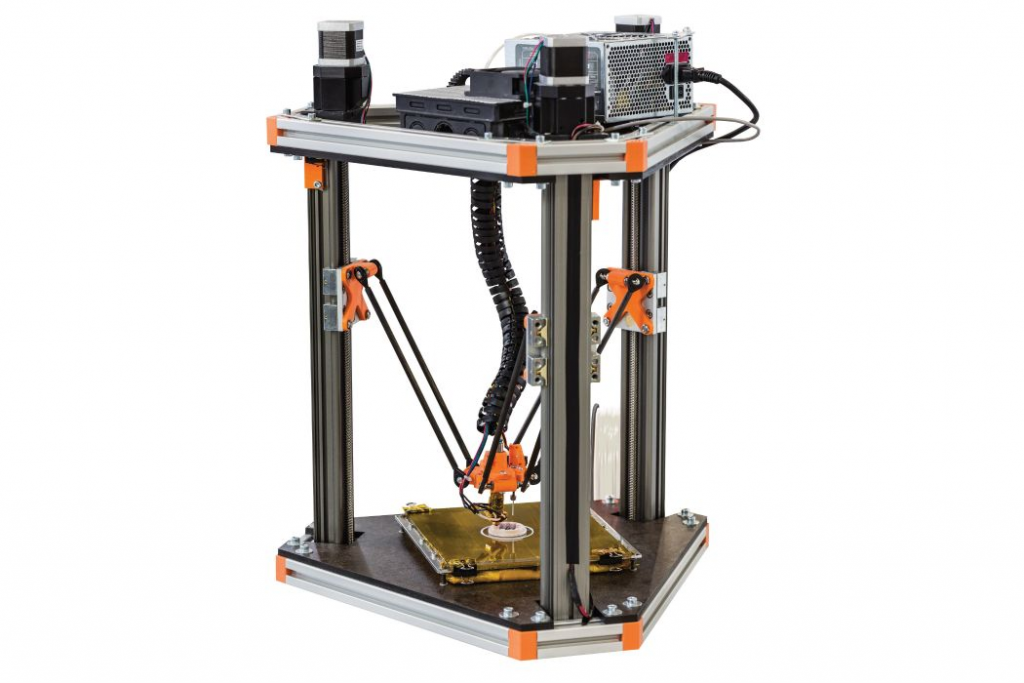
What is the FDM method?
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a 3D printing method whereby a material such as plastic is melted to create a 3D object layer by layer. Fused Deposition Modeling is an additive manufacturing method and is also referred to as the fused layer modeling method. The plastic or metal material that is processed is called filament.
The filament must reach a liquid state so that the individual layers of the model can be added. The filament is heated accordingly and forced through a fine nozzle. This produces a thin thread of plastic, which is used to make layers that are placed one on top of the other to finally end up with a 3D component.
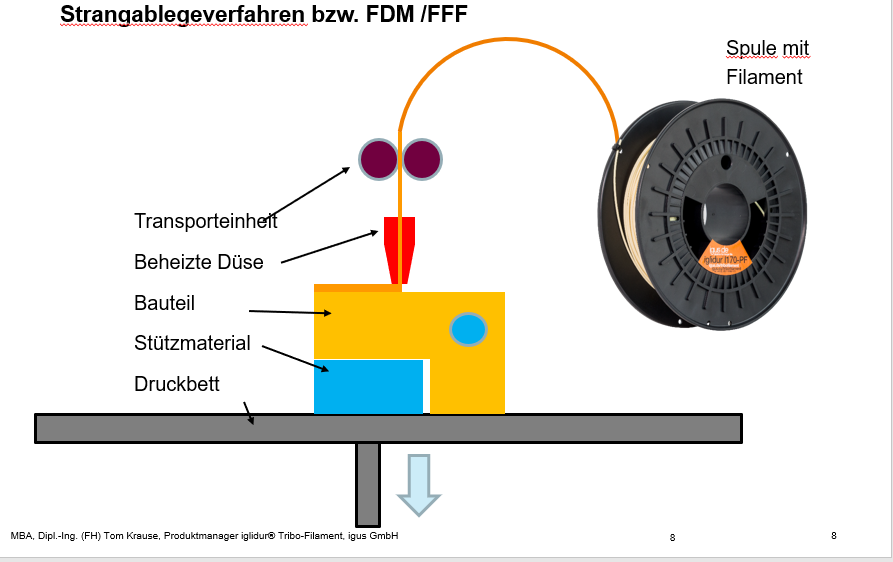
Depending on the application in which the printed component is to be used, different plastics can be used. This ranges from simple PLA (polylactide) to high-performance polymers for heavy-duty applications in moving parts.
Frequent areas of use for the FDM method in 3D printing:
- Prototype manufacturing
- Medical technology
- Tooling technology
- Aviation & aerospace
- Components for complex testing procedures
- High temperature applications

